Discovering unfamiliar spots on your skin or your child’s skin can be concerning, which is why it’s important to know the difference between a skin rash and petechiae.
Petechiae are small, round dots of bleeding that form under the skin or mucous membranes.
Though petechiae are common, they can have several different causes, some of which can be serious.
In this article, we’ll go over what petechiae are and how to distinguish them from a skin rash. We’ll also cover the most common places petechiae occur and what can cause them.
Finally, we’ll explain what you can do to prevent them and when to reach out to a healthcare provider for diagnosis and treatment.
What Are Petechiae?
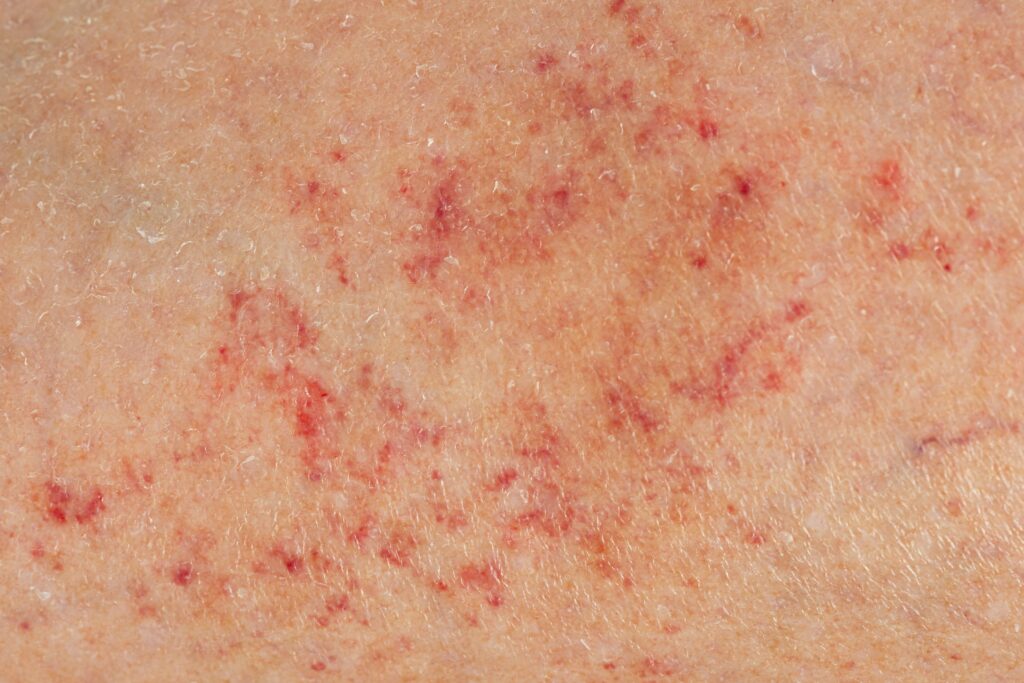
Petechiae are pinpoint-sized spots that appear under the skin or mucous membranes.
They are the result of bleeding which can be caused by several factors including injury, infection, and noninfectious medical conditions.
What they look like
Petechiae are very small and measure less than 2 mm in size. They can be red, brown, or purple in color.
Unlike other skin conditions, they are not raised or bumpy and do not lose color when you press or touch them.
Petechiae vs. Skin Rash
Because petechiae can appear in clusters, they are often confused for a skin rash, but petechiae are not rashes. They are dots that form under the skin or mucous membranes caused by broken blood vessels.
Here are some of the main differences between petechiae and skin rashes:
| Presentation | Petechiae | Skin Rash |
| Can cause itchiness | No | Yes |
| Can cause pain | No | Yes |
| Will turn pale or lighter in color when touched | No | Yes |
| Mostly flat to the touch | Yes | No |
Where Can Petechiae Occur?
Petechiae can occur anywhere on the body, but some of the most common areas in which petechiae occur are:
- Arms
- Butt
- Inside of the eyelids
- Legs
- Mouth
- Stomach
Causes
Petechiae are formed when capillaries (small blood vessels) bleed and leak blood into the skin. There are several possible causes of this type of bleeding, with some more serious than others.
Physical trauma
Accidental and non-accidental Injuries can cause bleeding, which can lead to petechiae.
Types of physical trauma that can result in petechiae include:
- Car accident
- Bite
- Friction on the skin
- Sunburn
- Prolonged straining (as a result of chronic coughing, vomiting, giving birth, etc.)
Non-infectious conditions
Petechiae can also be caused by non-infectious medical conditions.
Types of medical conditions that can cause petechiae include inflammatory, congenital, hematological, and connective tissue disorders such as those listed below:
- Leukemia
- Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP)
- Thrombocytopenia with absent radius (TAR) syndrome
- Fanconi anemia
- Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
- Haemolytic uraemic syndrome (HUS)
- Splenomegaly
- Neonatal alloimmune thrombocytopenia (NAIT)
- Henoch-Schonlein purpura (HSP)
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
- Vasculitis
- Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
- Glanzmann thrombasthenia
- Bernard-Soulier syndrome
- Medication reactions
- Vitamin K deficiency
- Vitamin C deficiency (scurvy)
- Chronic liver disease
Infectious conditions
Petechiae can also be caused by fungal, viral, or bacterial infections, such as:
- Congenital TORCH
- Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection
- Dengue
- Endocarditis
- Enterovirus
- Meningococcemia
- Mononucleosis
- Parvovirus
- Rocky Mountain spotted fever
- Scarlet fever
- Sepsis
- Strep throat
- Viral hemorrhagic fevers
See a doctor online.
Start my visitPrevention
With so many possible causes of petechiae, it’s not always possible to prevent them.
However, there are some actions that may help:
- Personal hygiene: Avoid contact with people who are sick, wash hands frequently and thoroughly with water and soap, clean and sanitize high- touch surfaces (including door handles, kitchen countertops, faucets, etc.), and don’t share personal items that touch your nose and mouth.
- Sun protection: Wear sunscreen and protective clothing and/or prioritize shade when exposed to the sun.
- Tick prevention: Wear long clothing (especially long socks and pants) and insect repellent when spending time in the woods and areas with tall grass. Always check your body for ticks after spending time in wooded or grassy areas.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of petechiae will require a physical evaluation of your skin by your healthcare provider. In addition to asking about additional symptoms, your provider may order testing to aid their diagnosis, such as:
- Complete blood count (CBC) to check platelet numbers
- Renal, liver, and coagulation profiles
- Urine test
Treatment
In several cases, petechiae may not require specialized treatment and can be taken care of at home.
Home remedies for petechiae include cold compresses, rest, and fluids.
However, if your petechiae are caused by a more serious condition, your provider may recommend one of the following, depending on the cause:
- Antibiotics
- Corticosteroids
- Immunosuppressant medication
- Vitamin supplementation
- Chemotherapy, radiation, immunotherapy, or bone marrow transplant
See a doctor online.
Start my visitWhen To See a Medical Provider
In some cases, petechiae can be a sign of a serious condition that requires immediate medical attention.
If you notice any of the below symptoms, seek emergency medical attention right away:
- Confusion
- Dizziness
- Loss of consciousness
- High fever
- Difficulty breathing
How K Health Can Help
Did you know you can access online urgent care with K Health?
Check your symptoms, explore conditions and treatments, and if needed, text with a healthcare provider in minutes.
K Health’s AI-powered app is based on 20 years of clinical data.
K Health articles are all written and reviewed by MDs, PhDs, NPs, or PharmDs and are for informational purposes only. This information does not constitute and should not be relied on for professional medical advice. Always talk to your doctor about the risks and benefits of any treatment.
K Health has strict sourcing guidelines and relies on peer-reviewed studies, academic research institutions, and medical associations. We avoid using tertiary references.

 Medically reviewed
Medically reviewed